1. Introduction: Reaction Force (object stationary on a horizontal surface)
1. Reaction Force: The story of the box and the table
Imagine a box placed on a table. If the table disappears, the box falls, so the table exerts a force on the box.
This force is called: reaction force. This force is exerted by the table on the box.
To be clear, we are studying the box, this is what we call the system.
The value of the reaction force is denoted R, so the vector R→ represents this force.
Initially, the object is stationary, placed on a horizontal surface.
2. Reaction Force: The 4 characteristics
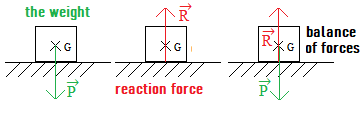
In this situation, what does the reaction force do?
The reaction force compensates for the weight.
It therefore has the same value, with an opposite direction.
It therefore has the same value, with an opposite direction.
The reaction force R→ can be represented by the 4 characteristics:
- point of application: center of the contact surface between the box and the table
- direction: vertical
- sense: upwards
- value ?:
2. Representing the reaction force (without friction)
TEST: 0 / 5
Goal: represent the force R→ for an object with mass m = g.
- System: a box placed on the table
- Earth Reference Frame
- The system is stationary on a horizontal surface.
1. Choose a scale
2. Using the mouse, adjust the length of the vector R→
Data: acceleration due to gravity: g = 9.81 N/kg.
SuperCalculator 😁
÷
=
x
=
🔼 drag / drop 🔼
9.81
0.5
2
4
5
10
No, it's not finished! 🥺
Adjust the length of the vector.
Then lock the length with a left click.
▶️
scale
0.5 N/cm
2 N/cm
4 N/cm
5 N/cm
10 N/cm
◀️
No, it's not finished! 🥺
Choose a scale.
▶️
3. Reaction (with friction)
a. Defining R→:
In this situation (blue box placed on an inclined surface),
how do you describe the action of the support?
how do you describe the action of the support?
We can identify 2 actions:
- The inclined plane prevents the box from falling: R→N
- Friction opposes movement: R→T
b. The 4 characteristics of R→N:
R→N is the normal reaction (normal means perpendicular), its 4 characteristics:
- Point of application: center of the contact surface between the table and the box
- Direction: perpendicular to the support
- Sense: upwards
- Value: ?
c. The 4 characteristics of R→T:
R→T is the friction force, it opposes movement:
- Point of application: center of the contact surface between the table and the box
- Direction: parallel to the support
- Sense: to the left (opposite to the movement)
- Value: ?
d. And the value?
There is no formula to directly calculate the values of the above forces, but they can be experimentally determined.
We can also determine these forces in the case where the box is stationary if we know its mass (see activity 3).
In the case where the blue box is stationary, what can be said about the weight of the box and the reaction of the support?
The weight and the reaction force compensate each other:
- R = P = mg
- R→ = R→N + R→T = - P→